Memory is critical for system performance. As DDR5 gains ground after DDR4's long reign, understanding their differences helps in informed upgrading or building decisions.
DDR4 launched with 2133-2400MHz, later reaching up to 4266MHz+ for high-end models. DDR5 starts at 4800MHz (surpassing DDR4's peak) and now hits 8000MHz+, boosting data transmission speed.
DDR4 runs at 1.2V; DDR5 drops to 1.1V, cutting power use by ~8%. This saves energy, lowers costs, and extends laptop battery life.
DDR4 3200 offers 25.6GBps, while DDR5 4800 delivers 38.4GBps. Faster bandwidth speeds up large data tasks like gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering.
Memory Type | Frequency Range | Voltage | Typical Bandwidth |
DDR4 | 2133-4266MHz+ | 1.2V | 25.6GBps (3200MHz) |
DDR5 | 4800-8000MHz+ | 1.1V | 38.4GBps (4800MHz) |
DDR4-2666 has CL17-19; DDR5-4800 typically uses CL40, leading to higher initial latency. Yet, DDR5's higher frequency still outperforms DDR4 overall.
DDR4 relies on motherboard-based PMICs; DDR5 integrates PMICs on the memory PCB, enhancing power stability and reducing motherboard load.
DDR5's 16GB per chip (vs. DDR4's 4GB) enables larger single sticks (up to 256GB+ theoretically). Consumer options now include 16GB/32GB sticks, fitting more capacity in fewer slots.
Different notch positions mean DDR4 and DDR5 are physically incompatible. Motherboards require matching slots.
DDR5 adds On-die ECC (corrects internal errors only), unlike traditional ECC (fixes operational errors), boosting stability.
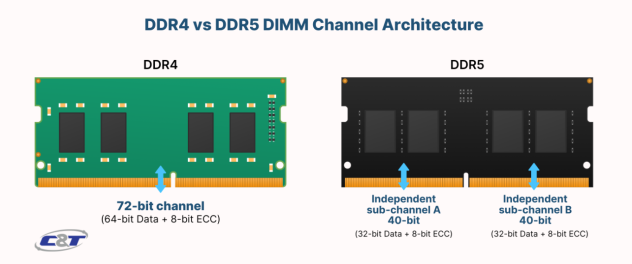
DDR4 needs two sticks for dual-channel; DDR5 can mimic it with one (via split 64Bit channel). Two sticks still perform best.
DDR5's XMP3.0 offers 5 profiles (3 fixed, 2 custom) with voltage control and user-friendly software, simplifying overclocking.
Motherboard Match: Ensure compatibility with your motherboard's slots.
Budget: DDR5 and supporting motherboards cost more; DDR4 remains cost-effective for basic needs.
Usage: DDR5 excels in heavy tasks (video editing, gaming); DDR4 suffices for daily use (browsing, office work).
In short, DDR5 outperforms DDR4 in speed, efficiency, and features but costs more. Choose based on compatibility, budget, and usage demands.