If you’ve ever felt that your mouse moves too fast or too slow on the screen, DPI is likely the key factor behind this experience. Let’s break down what DPI means for your mouse and how you can adjust it to match your needs.

DPI stands for “Dots Per Inch”. In simple terms, it measures how sensitive your mouse is to movement: a higher DPI means the cursor moves farther on the screen with the same physical mouse movement, while a lower DPI results in slower, more precise cursor movement.
For example, if your mouse is set to 800 DPI, moving it 1 inch across your desk will make the cursor travel 800 pixels on the screen. At 1600 DPI, that same 1-inch movement will move the cursor 1600 pixels—twice as far. This makes DPI a critical setting for tasks like gaming (where precision or speed matters) or graphic design (where fine control is essential).
It’s important to note that DPI is different from “sensitivity,” a term often used in software or games. Sensitivity adjusts how the operating system or game interprets the mouse’s DPI, but DPI itself is a hardware-based measurement of the mouse’s sensor capability.
The method to adjust DPI depends on your mouse’s design and whether it has dedicated features. Here are the most common ways:
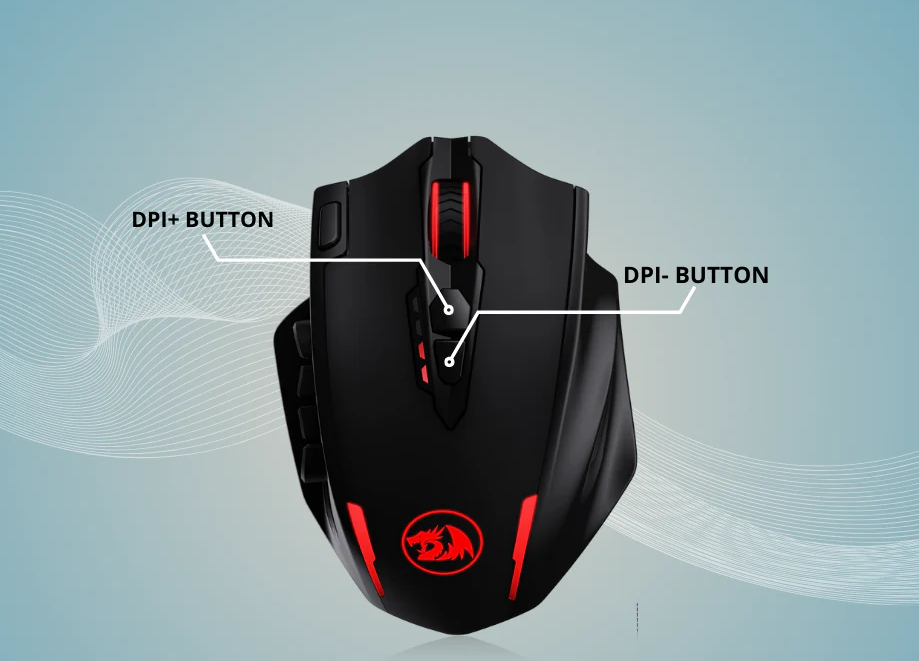
Many modern gaming or advanced mice come with built-in DPI buttons (usually labeled or located near the scroll wheel). These buttons let you cycle through preset DPI levels instantly.
How to use: Press the DPI button, and you may see a light indicator (e.g., different colors or blinking patterns) that shows the current DPI level. Check your mouse’s manual to match the lights to specific DPI values (e.g., red = 800 DPI, green = 1600 DPI).
This is the fastest way to switch DPI, especially useful during activities like gaming where you might need quick adjustments (e.g., lower DPI for aiming, higher DPI for navigating large maps).
Most branded mice (such as Logitech, Razer, or Corsair) come with companion software (e.g., Logitech G HUB, Razer Synapse). This software lets you customize DPI levels in detail:
Steps: Install the software from the manufacturer’s website, connect your mouse, and look for a “DPI” or “Sensitivity” tab. Here, you can set exact DPI values (e.g., 400, 800, 1200), create presets, or even adjust DPI separately for horizontal and vertical movement.
Some software also lets you link DPI settings to specific apps or games, ensuring optimal sensitivity for each task.

If your mouse doesn’t have dedicated buttons or software, you can adjust cursor speed through your computer’s settings. While this isn’t technically changing DPI (it’s adjusting how the OS interprets the mouse’s input), it achieves a similar effect:
Windows: Go to “Settings > Devices > Mouse” and use the “Mouse pointer speed” slider to make the cursor faster or slower.
macOS: Open “System Preferences > Mouse” and adjust the “Tracking speed” slider.
Keep in mind that this method affects all mouse input, so it’s a basic solution for casual use rather than precise DPI control.
The “best” DPI depends on your activity and personal preference:
Gaming: FPS players often prefer 400–800 DPI for precise aiming, while MMO or strategy gamers may use 1000–1600 DPI for faster navigation.
Productivity: 800–1200 DPI works well for everyday tasks like browsing or document editing.
Graphic Design/Photo Editing: Lower DPI (400–800) helps with fine cursor control when working on detailed projects.
Experiment with different settings to find what feels comfortable. Remember, consistency matters more than a specific number—stick to a DPI that lets you move the cursor smoothly without overshooting targets.
In summary, DPI determines how responsive your mouse is to movement, and adjusting it is key to a better user experience. Whether you use hardware buttons, software, or OS settings, finding the right DPI can make tasks feel more intuitive and precise.