As the "heart" of a computer, the power supply generates significant heat during operation, and the fan is crucial for cooling. Incorrect orientation can lead to:
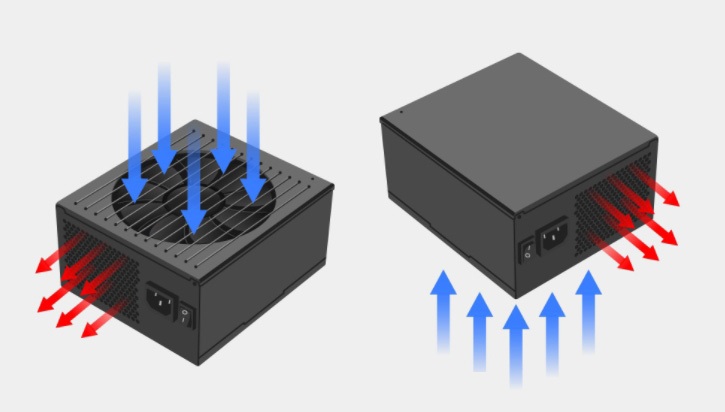
Reduced cooling efficiency: Disordered airflow raises internal temperatures, potentially shortening the lifespan of capacitors and components.
Faster dust accumulation: Wrong airflow directions allow dust to enter the power supply, affecting cooling and risking short circuits.
Increased noise: Obstructed airflow may cause abnormal fan speeds and noticeable noise.
Cases with bottom ventilation holes: Common in mid-tower/full-tower cases, where downward-facing fans expel heat directly through bottom holes.
High dust prevention needs: Since dust mostly enters from the top or sides, a downward fan "protects" internal components from accumulation.
A leading ATX power supply manual recommends downward installation when the case has a bottom dust filter, aligning with a "bottom-in, top-out" airflow cycle.
Cases with top cooling designs: Premium cases with top fans/holes allow upward-facing fans to form a "vertical airflow channel" with top fans.
Power supplies with built-in dust filters: Removable filters on the fan side make upward installation easier for regular cleaning.
Never install upward without a dust filter—tests show dust accumulation is 4 times higher than downward installation within 3 months.
| Case Type | Bottom Vents | Top Vents | Recommended Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Mid-Tower | Yes | No | Downward |
| High-End Side-Panel Case | Yes | Yes | Upward (with top fans) |
| Mini ITX Case | No | Yes | Upward (prioritize cooling in limited space) |
Some PSUs mark "OUT" arrows on the fan side (indicating airflow direction); an arrow pointing down means install the fan downward.
If the PSU has a removable dust filter, prefer upward installation for easy cleaning.
Before installation, power on the case (safely!) and hold a tissue near the fan—ensure the airflow aligns with the case's ventilation path (e.g., bottom intake, top exhaust).
Power off and discharge: Unplug the power cord and press the power button to release residual electricity.
Secure the PSU: Place the PSU in the case, fix it with screws (tighten to avoid vibration noise), fan side facing down.
Cable management: Route cables at least 5cm away from the fan to prevent obstruction.
Monthly dusting: Use compressed air to blow from the inside of the PSU (opposite the fan) to remove dust (never use a wet cloth).
Quarterly inspection: Check for fan 卡顿 (normal speed: 1200-2000 RPM). Add minimal lubricant to oil-bearing fans if speeds slow.
Annual replacement: Replace fans or the entire PSU after 3 years (aging bearings may cause noise).
Fact: Tests show incorrect orientation raises internal temperatures by 15-20℃, potentially triggering overheat protection in summer.
Solution: Use a $3 magnetic dust filter over the fan, rinsing monthly to reduce dust by 80%.
Troubleshooting:
Check dust accumulation (over 30% dust increases noise).
If noise persists after cleaning, replace the fan (cost: $10-20).
Rack-mounted servers often use "front-to-rear" airflow, with fans facing forward to align with cabinet air conditioning.
During overclocking, install the fan downward and add a 12cm bottom case fan (1500+ RPM) for dual-fan direct cooling.
Choose a low-RPM fan (e.g., 14cm fan ≤1500 RPM) with an upward-facing dust filter to balance cooling and noise (<25dB).
Conclusion: Fan orientation isn’t one-size-fits-all—adjust based on case structure and environment. Mastering these principles extends PSU life and reduces PC failures, as stable power is the foundation of hardware performance.