Choosing the right PC case is an essential step when building a personal computer. The case not only affects the cooling performance, appearance, and expandability of your hardware, but it also directly influences the overall user experience. Therefore, understanding the characteristics of different case sizes and how to choose the right case based on the motherboard and hardware configuration is crucial for creating a well-performing and aesthetically pleasing computer.
When selecting a case, you’ll typically encounter a few common standard sizes: ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX. Each size has its own advantages and limitations, catering to different user needs and hardware setups.
This article will explore the differences between these common case sizes and help you choose the right case based on your motherboard and hardware configuration.
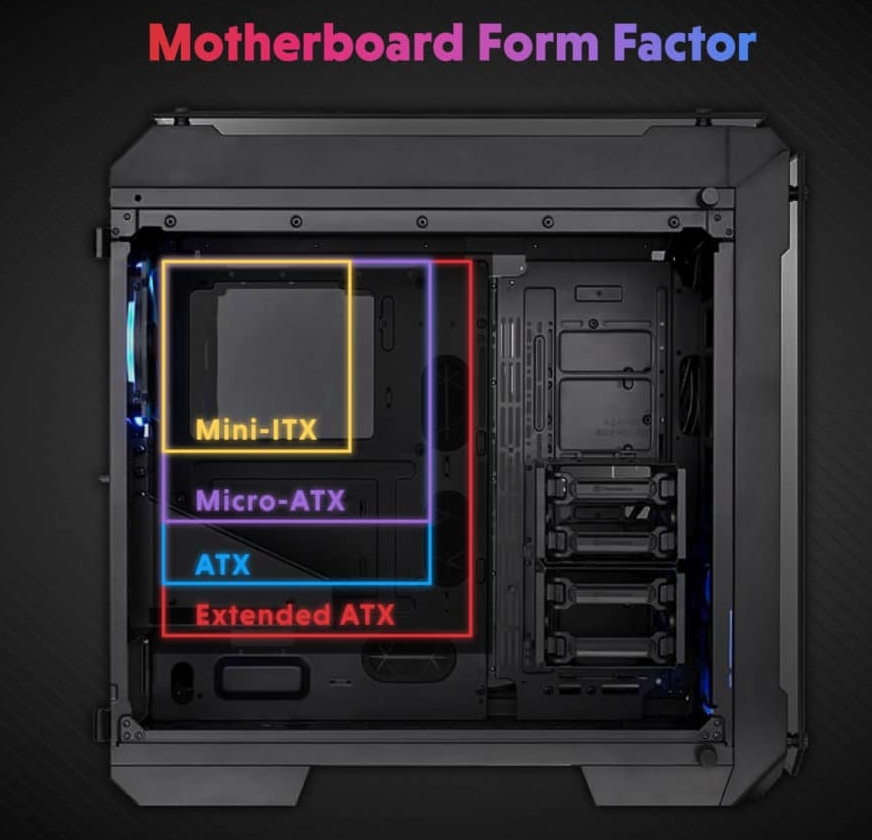
PC cases are generally categorized based on motherboard standards. The size of the motherboard determines the internal space required for the case, and the case size directly affects the installation space for hardware, cooling design, expandability, and overall appearance.
Dimensions: Approximately 305mm x 330mm x 520mm (W x H x D)
ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended) is one of the most common standards and is widely used in desktop computers, especially for those that require high performance and multiple hardware expansion slots. ATX cases generally provide more space, supporting various hardware configurations, particularly large graphics cards, multiple storage devices, and complex cooling systems.
Advantages:
Spacious: ATX cases offer enough space to accommodate most hardware, such as large graphics cards, multiple storage devices, and complex cooling systems.
Strong Expandability: ATX cases usually come with multiple expansion slots, supporting extra PCI cards, sound cards, etc.
Better Cooling: Due to the larger internal space, airflow is less restricted, which often allows for better cooling, especially for high-power systems.
Disadvantages:
Larger Size: ATX cases are bigger than Micro-ATX and Mini-ITX cases, taking up more desk space, which may not be ideal for users with limited room.
Dimensions: Approximately 244mm x 244mm x 400mm (W x H x D)
Micro-ATX cases are smaller than standard ATX cases and are suitable for users who don’t require a lot of expansion but still want enough performance. Micro-ATX motherboards are smaller in size, but still provide multiple expansion slots, making them ideal for office or home entertainment setups.
Advantages:
Compact Design: Micro-ATX cases are smaller than ATX cases and are perfect for environments with limited desk space.
Good Performance Balance: Despite being smaller, Micro-ATX cases can still support most hardware configurations and provide good overall performance.
Cost-Effective: Micro-ATX cases are generally less expensive than ATX cases, making them an excellent choice for budget-conscious users.
Disadvantages:
Limited Expandability: While there are multiple expansion slots, the expandability of Micro-ATX cases is still much less than ATX cases, limiting upgrade and expansion options.
Limited Space: Due to the smaller size, there may be restrictions on large graphics cards or advanced cooling solutions.
Dimensions: Approximately 170mm x 170mm x 300mm (W x H x D)
Mini-ITX is the smallest case standard and is designed for users who need to save space. It is ideal for building compact systems, such as HTPCs (Home Theater PCs), mini desktop PCs, and so on. The Mini-ITX motherboard has only one expansion slot, so hardware options are limited, making it suitable for lightweight use cases.
Advantages:
Extremely Compact: Mini-ITX cases are very small, making them perfect for limited-space environments like small desks or living room setups.
Portability: Due to their small size, Mini-ITX cases are highly portable and easy to move, ideal for users who need a computer they can carry around.
Low Power Consumption: Systems built with Mini-ITX motherboards tend to be more energy-efficient, making them great for building low-power home entertainment PCs or compact office desktops.
Disadvantages:
Limited Expandability: Mini-ITX cases only support one expansion slot, so your hardware choices are more constrained.
Restricted Space: Due to the small size, there’s limited space for cooling solutions, which could be problematic when installing high-performance graphics cards or complex cooling systems.
Limited Hardware Choices: The small case size means you’ll have to choose smaller hardware components, such as compact graphics cards or cooling systems.

When choosing the right PC case, the first thing to consider is the motherboard size. Common motherboard standards include ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX. Different motherboard sizes require different case spaces, and here’s a basic guide to choosing a case based on your motherboard size:
For ATX Motherboards:
If you choose an ATX motherboard, it’s recommended to go for an ATX case. An ATX case provides enough space to accommodate all the components of an ATX motherboard, and it can support multiple expansion slots, graphics cards, and storage devices.
When selecting an ATX case, make sure it has enough internal room for multiple storage bays, graphics cards, and adequate cooling options (e.g., fans or water cooling systems).
For Micro-ATX Motherboards:
If you choose a Micro-ATX motherboard, opt for a Micro-ATX case. Micro-ATX cases are slightly smaller than ATX cases but still provide enough space for most hardware configurations.
Micro-ATX cases are an ideal choice for users who want a balance of performance and compact design, especially if you need a system with moderate expandability but don’t require a lot of space.
For Mini-ITX Motherboards:
For Mini-ITX motherboards, a Mini-ITX case is the best choice. Mini-ITX cases are very compact, ideal for building small-form-factor systems.
Keep in mind that due to the small size, you’ll need to choose hardware that fits within the limited space, and this could mean opting for compact graphics cards and cooling systems.
In addition to the motherboard size, you should also consider the size and configuration of your other hardware components when choosing a case. Different hardware components will place different demands on the case in terms of space and cooling design.
The size of your graphics card is an important factor in selecting the right case. High-performance graphics cards are often larger and require more space, which might require specialized cooling designs.
If you’re using a large graphics card, especially one with multiple fans, it’s best to go for an ATX case. Micro-ATX and Mini-ITX cases may not be able to accommodate larger or wider graphics cards.
Depending on the cooling requirements of your system, you’ll need to select an appropriate case. ATX cases usually support larger fans and more advanced water cooling solutions, while Micro-ATX and Mini-ITX cases may only support smaller fans or limited water cooling components.
If you plan to use high-performance processors (such as Intel i9 or AMD Ryzen 9) and graphics cards, it’s advisable to choose a case with good cooling performance, especially for smaller cases where cooling space is limited.
If you plan to use multiple storage devices (e.g., HDD and SSD configurations), an ATX case will provide more hard drive bays and make it easier to install multiple storage devices.
Micro-ATX and Mini-ITX cases are better suited for users who need fewer storage devices. Keep in mind that small cases may require 3.5-inch to 2.5-inch drive adapters to save space.
Choosing the right PC case is not just about considering its size; you also need to factor in your hardware configuration, cooling needs, and expandability. For most general users or office setups, Micro-ATX and Mini-ITX cases are sufficient. However, for users needing high-performance hardware and more room for expansion, an ATX case is often the best choice.
Regardless of the case size, ensure it meets your needs in terms of space, cooling performance, and the ability to house the hardware you plan to install. The right case will not only house your components but also contribute to the overall functionality and aesthetics of your computer.