When it comes to building a custom PC, one of the most critical factors to consider is cooling performance. Efficient heat dissipation ensures that your components run at optimal temperatures, prolonging their lifespan and maintaining peak performance. The case you choose plays a vital role in how well heat is managed within your system.
In this article, we will guide you through evaluating the cooling capabilities of a PC case. We will explore how to assess the case’s airflow design, fan support, ventilation options, and other cooling factors that contribute to keeping your system cool and stable.
The central processing unit (CPU), graphics processing unit (GPU), and other components of your PC generate significant heat during operation. If this heat isn’t properly dissipated, it can lead to thermal throttling (where components slow down to prevent overheating), reduced lifespan of hardware, and even system instability or crashes.
A well-designed PC case ensures that these components have enough airflow to maintain safe operating temperatures. Proper cooling prevents overheating, enhances performance, and helps reduce the noise levels generated by overheating components.
To evaluate the cooling capabilities of a PC case, we must consider several factors, including airflow design, fan support, the quality of ventilation, and the possibility for additional cooling solutions such as liquid cooling. Let’s take a look at these in detail.
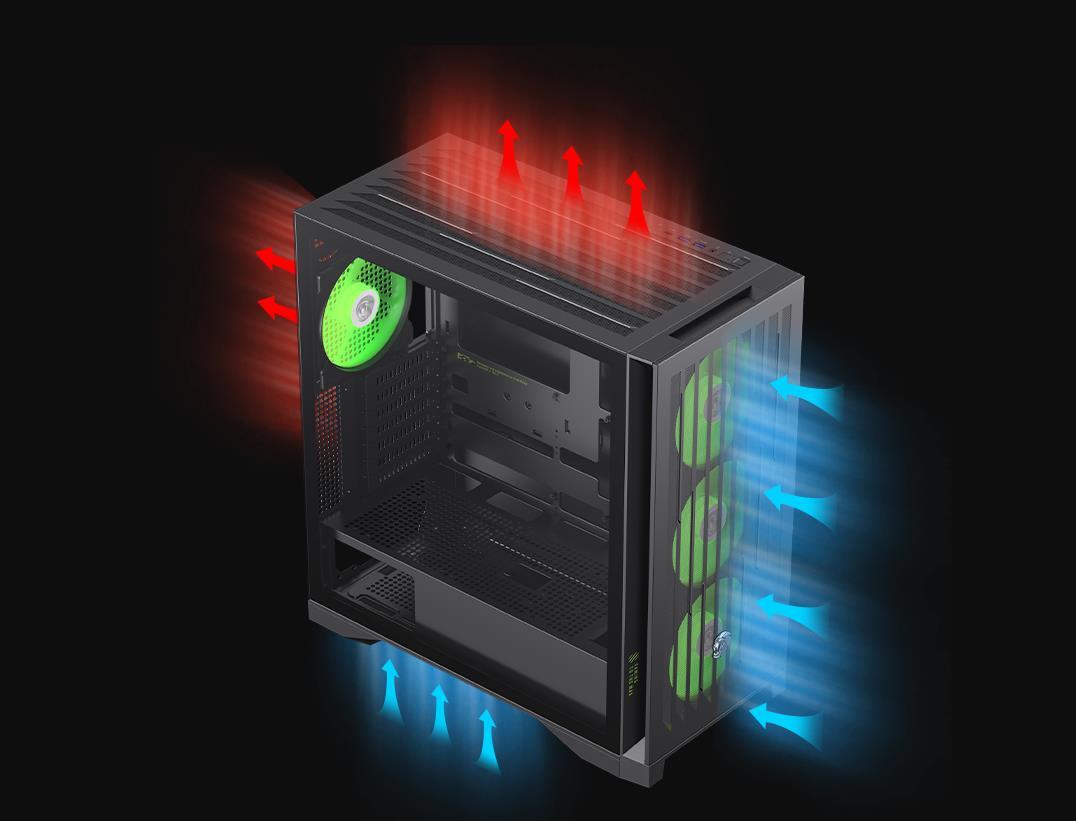
The airflow design is arguably the most crucial element when determining how well a case will cool your system. A case that supports good airflow ensures that cool air enters the system and hot air exits effectively.
Front-to-Back Airflow:
Most PC cases are designed with front-to-back airflow in mind, which means cool air is pulled in through the front of the case and hot air is exhausted out through the back. This is the most efficient airflow direction as it follows the natural flow of hot air rising, and the rear exhaust fan ensures that heat is actively pulled out of the case.
Bottom-to-Top Airflow:
Some cases include bottom-mounted intake fans and top-mounted exhaust fans. This design allows for additional airflow, as the intake fans draw in cool air from the bottom while the top exhaust fans expel hot air rising naturally.
Positive vs. Negative Pressure:
Pressure within the case is another key factor. Positive pressure occurs when more intake fans are used than exhaust fans, resulting in a slight push of air out of the case. This helps prevent dust from entering but might slightly reduce cooling efficiency. Negative pressure occurs when there are more exhaust fans than intake fans, which can improve cooling but may cause dust to accumulate inside the case.
When evaluating airflow, make sure the case has designated intake and exhaust areas that are not obstructed, ensuring the effective flow of air. Look for cases with mesh panels or other ventilation features to optimize airflow.

The number of fans a case can support, as well as their size and placement, significantly impacts the cooling performance. A case that supports more fans can distribute airflow more effectively, cooling different components simultaneously.
Fan Size:
Larger fans (such as 140mm or 200mm) are often more efficient at moving air at lower speeds compared to smaller 120mm fans. If the case supports larger fan sizes, it can reduce the overall noise level while still providing excellent cooling performance.
Fan Mounts:
When evaluating fan support, check the case’s layout to see how many fans it can accommodate. Cases typically offer mounts for front, top, and rear fans. Some also have additional spots for bottom-mounted fans. Make sure the case supports the number of fans required for your cooling setup.
Fan Speed and Control:
Not all fans are created equal. Some come with adjustable speeds or RGB lighting, while others may feature quieter or more powerful options. Consider whether you want PWM (pulse-width modulation) fans that can adjust their speed based on temperature readings, helping maintain a balance between cooling and noise levels.
Ventilation is critical to cooling performance. A PC case with excellent ventilation helps ensure that hot air doesn’t get trapped inside and cool air can circulate freely. When choosing a case, you should pay attention to the following factors:
Mesh panels on the front, top, and bottom of a case allow for better airflow compared to solid panels. Mesh designs reduce airflow resistance and allow cool air to enter easily while letting hot air escape.
Cases with solid panels may have limited ventilation, especially if they are designed for a sleek and minimalist appearance. While these cases look good, they often don't provide the same level of cooling performance as cases with mesh or perforated designs.
Dust filters are an essential feature for PC cases, especially for those with mesh or open panel designs. Without filters, dust can accumulate inside the case, clogging up the fans and vents, reducing airflow, and potentially causing hardware to overheat.
Many modern cases come with removable filters for the front, bottom, and top panels. Ensure that the case has a dust filtration system in place to help maintain airflow efficiency.
In addition to regular fans, many modern cases support additional cooling solutions such as liquid cooling (both AIO and custom loops), which can offer superior cooling performance, especially for high-end gaming PCs or workstations.
Cases designed for liquid cooling typically have mounts for radiators, either on the top, front, or bottom of the case. Some cases even allow you to install a full custom liquid cooling loop for maximum cooling efficiency. For users planning to overclock their CPU or GPU, liquid cooling can help maintain safe temperatures even under heavy load.
Radiator Support:
When assessing liquid cooling compatibility, check whether the case can accommodate the size of the radiator you plan to install. Common radiator sizes are 120mm, 240mm, and 360mm, with larger radiators offering better cooling performance.
For users who need extra cooling, some cases offer additional space for mounting additional fan brackets, or allow the installation of more advanced cooling systems. For example, support for VRM cooling or chipset cooling may be available in higher-end cases. Make sure to choose a case that supports your specific cooling setup.
While airflow design, fan support, and ventilation are key factors in cooling performance, here are a few additional considerations that can further optimize your system’s cooling efficiency:
A cluttered case can obstruct airflow, making it harder for cool air to reach critical components like the CPU and GPU. Look for cases that offer excellent cable management options, such as cable-routing channels, tie-down points, and hidden compartments for cables. A well-managed case helps improve airflow and keeps components cool.
The material of the case can influence its cooling performance as well. Steel and aluminum cases are durable and typically have good heat dissipation properties. Plastic cases may not offer the same level of heat dissipation, but they often provide better insulation and may reduce external temperatures.
External devices such as external cooling fans or air conditioning units can be used to complement the cooling system in your PC case, particularly in high-performance environments. However, this is an added measure, not a necessity, and shouldn’t be relied upon as the primary cooling method.
A good PC case is fundamental to keeping your system running cool and stable, particularly if you’re using high-performance components or planning to overclock. When selecting a case, evaluate the airflow design, fan support, ventilation options, and compatibility with additional cooling solutions.
By understanding the cooling potential of different cases and making informed decisions based on your specific hardware and cooling needs, you can ensure that your PC remains cool, efficient, and quiet, even under heavy loads. Ultimately, a well-cooled PC is one that performs better, lasts longer, and provides a smoother experience for both work and play.