RAM is critical for your PC’s performance. Knowing its speed, size, and type helps with upgrades and troubleshooting. Here are simple methods to check these details in Windows.
A quick built-in tool for basic RAM info:
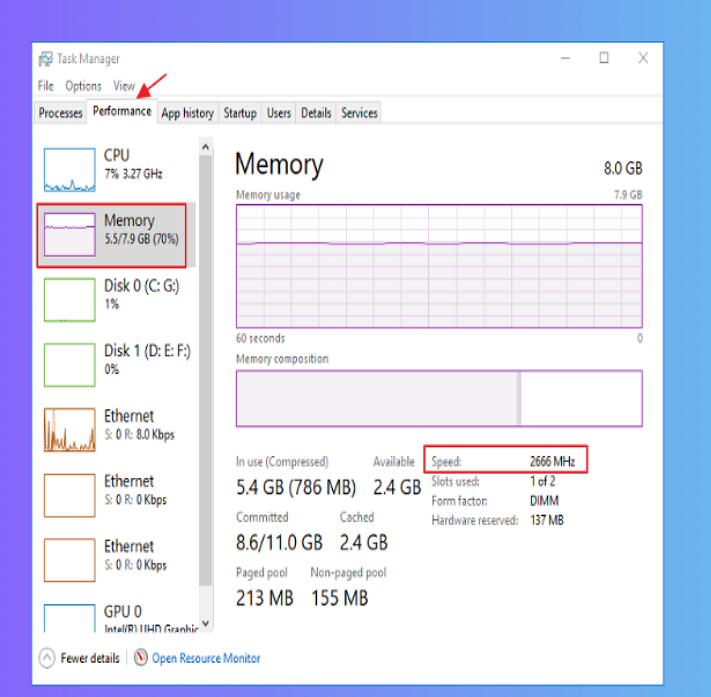
Open Task Manager with Ctrl + Shift + Esc, or right-click the taskbar and select it.
Go to the Performance tab, then click Memory on the left.
You’ll see:
Speed: RAM’s operating speed (e.g., 3200 MHz).
Size: Total installed RAM (e.g., 16 GB).
Note: RAM type (DDR4, DDR5) isn’t explicitly listed but can be inferred from speed (e.g., 2133–3200 MHz = likely DDR4).
For precise technical details via commands:
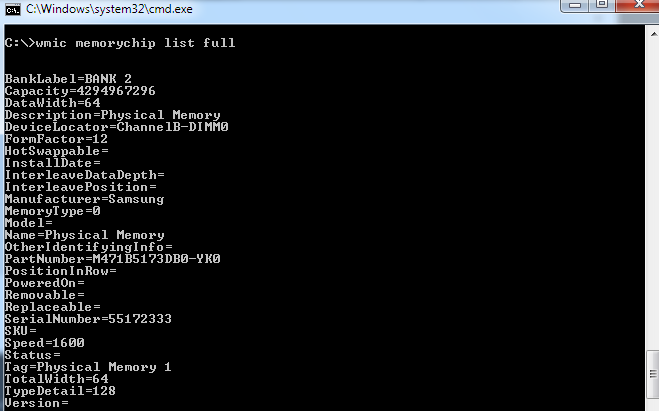
Open Command Prompt as Administrator (search “cmd,” right-click > “Run as admin”).
Use these commands:
Check speed: wmic memorychip get speed (shows MHz per module).
Check type: wmic memorychip get memorytype (returns a code; e.g., 28 = DDR4).
Full details: wmic memorychip list full (size, manufacturer, part number, etc.).
A free tool for detailed RAM specs:
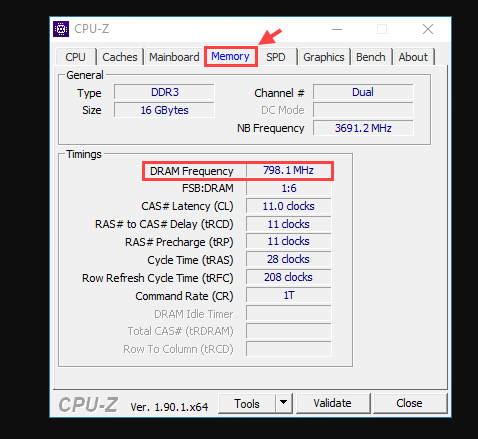
Download CPU-Z from the official site and install it.
Open CPU-Z and go to the Memory tab:
Type: Explicitly shows DDR3/DDR4/DDR5.
Speed: Multiply the “DRAM Frequency” by 2 to get the actual DDR speed (e.g., 1600 MHz × 2 = 3200 MHz).
Size & channels: Total RAM and whether it runs in dual-channel mode.
Another user-friendly option:
Download Speccy from Piriform’s site and install.
Open Speccy, expand Memory on the left. It shows:
Type (e.g., DDR5-4800), speed, total size, and even manufacturer/model.
For hardware-level info (useful if Windows tools fail):
Restart your PC and press the BIOS key during boot (usually Del, F2, or F10—check your motherboard manual).
Look for a “Memory” or “System Information” section to find speed, type, and size.
Upgrades: Ensure new RAM matches your system’s type (DDR4 vs. DDR5) and speed.
Troubleshooting: Slow performance may relate to underpowered RAM (e.g., low speed or insufficient size).
Use these methods to stay informed about your RAM and keep your PC running smoothly.